Maccd
(Created page with "{{DISPLAYTITLE:Maccd}} == 介绍 == <p>“MAC地址收集器”通过snmpwalk从可网管设备获取客户机的实际mac地址,从而使WFilter可以基于mac地址应用...") |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{DISPLAYTITLE: | + | {{DISPLAYTITLE:MAC Detector}} |
| − | == | + | == MAC Detector == |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | "MAC Detector" can gather client's physical MAC addresses via SNMP protocol. With "MAC Detector" enabled, you can: | |
| − | + | * Set access policy by MAC addresses. | |
| + | * Set IP-MAC binding in a multiple-segments network. | ||
| + | * Show real MAC addresses in "Real-time Bandwidth". | ||
| + | * Show real MAC addresses in "Internet Usage". | ||
| − | == | + | == Settings == |
| + | == SNMP Commands == | ||
| + | "MAC Detector" use snmpwalk commands to send SNMP query to manageable devices. Usually, the snmpwalk commands are sent to routing devices, for example: core three-layer switch, or manageable wireless AP. | ||
| + | * "SNMP Commands": snmpwalk commands be sent to the manageable devices. Multiple commands are supported. | ||
| + | * "Result Format": a regular expression which matches ONE record row. | ||
| − | + | === Example === | |
| − | + | Suppose the core three layer switch has ip address "192.168.1.2", the "SNMP Command" is: | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ''snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.2 ipNetToMediaPhysAddress'' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | ... | + | The real return message is: |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ''IP-MIB::ipNetToMediaPhysAddress.9.192.168.1.1 = STRING: 0:6:f6:bf:8b:cc'' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | [[ | + | ''IP-MIB::ipNetToMediaPhysAddress.9.192.168.1.11 = STRING: ae:15:53:a0:9b:7f'' |
| − | == | + | ... |
| − | + | ||
| − | [[ | + | |
| + | To match every return rows, we configure the "result format" as: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''IP-MIB::ipNetToMediaPhysAddress\.\d+.*'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
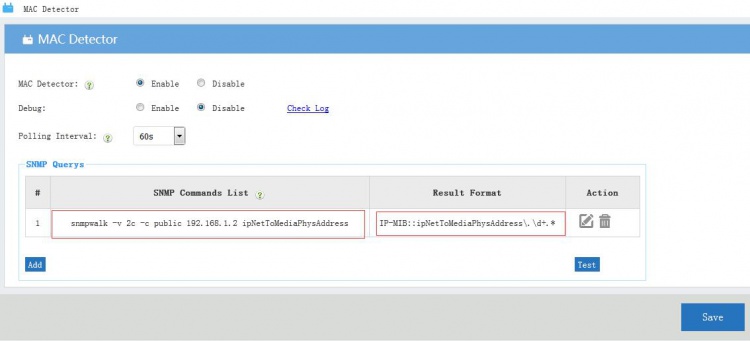
| + | The "MAC Detector" will use the "result format" to get every record and retrieve the mac and ip information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Maccd00.jpg|750px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Test === | ||
| + | |||
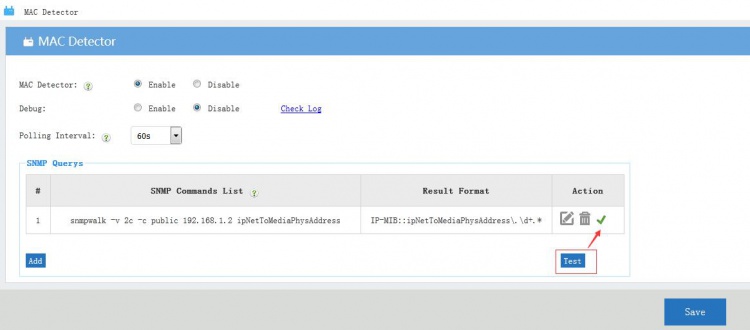
| + | You may click "test" to test the SNMP commands in the list. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Maccd01.jpg|750px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == FAQ == | ||
Latest revision as of 18:35, 24 December 2015
Contents |
[edit] 1 MAC Detector
"MAC Detector" can gather client's physical MAC addresses via SNMP protocol. With "MAC Detector" enabled, you can:
- Set access policy by MAC addresses.
- Set IP-MAC binding in a multiple-segments network.
- Show real MAC addresses in "Real-time Bandwidth".
- Show real MAC addresses in "Internet Usage".
[edit] 2 Settings
[edit] 3 SNMP Commands
"MAC Detector" use snmpwalk commands to send SNMP query to manageable devices. Usually, the snmpwalk commands are sent to routing devices, for example: core three-layer switch, or manageable wireless AP.
- "SNMP Commands": snmpwalk commands be sent to the manageable devices. Multiple commands are supported.
- "Result Format": a regular expression which matches ONE record row.
[edit] 3.1 Example
Suppose the core three layer switch has ip address "192.168.1.2", the "SNMP Command" is:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 192.168.1.2 ipNetToMediaPhysAddress
The real return message is:
IP-MIB::ipNetToMediaPhysAddress.9.192.168.1.1 = STRING: 0:6:f6:bf:8b:cc
IP-MIB::ipNetToMediaPhysAddress.9.192.168.1.11 = STRING: ae:15:53:a0:9b:7f ...
To match every return rows, we configure the "result format" as:
IP-MIB::ipNetToMediaPhysAddress\.\d+.*
The "MAC Detector" will use the "result format" to get every record and retrieve the mac and ip information.
[edit] 3.2 Test
You may click "test" to test the SNMP commands in the list.