Ipsecvpn
| (19 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:IPSec Tunnels}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE:IPSec Tunnels}} | ||
| − | == Tunnels == | + | == IPSec Tunnels == |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | == | + | This modules can build IPSec tunnels between multiple WFilter NGF networks, and make a secure site-to-site VPN. |
| + | The number of IPSec Tunnels depends on your hardware performance, there is no software limit on the tunnels number. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == IPSec Tunnel Settings == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Before you setup a IPSec tunnel, you need to design your tunnels. For example: | ||
| + | * Suppose you have 3 network: A, B, C. | ||
| + | * A has a static public IP, B and C ip addresses are dynamic. | ||
| + | The solution will be: | ||
| + | * A, B, C shall have differenct subnets. For example: 192.168.10.x, 192.168.20.x, 172.16.1.x. | ||
| + | * Create a tunnel in A network, set "Remote IP" to "Any". | ||
| + | * Create tunnels in B and C networks, set "Remote IP" to A's public ip address. | ||
| + | * Now the tunnels are ready. A, B, C now are in a VPN network. The tunnels are between AB and AC. | ||
| + | * To enable access between B and C, you need to enable FORWARD in A. | ||
| + | |||
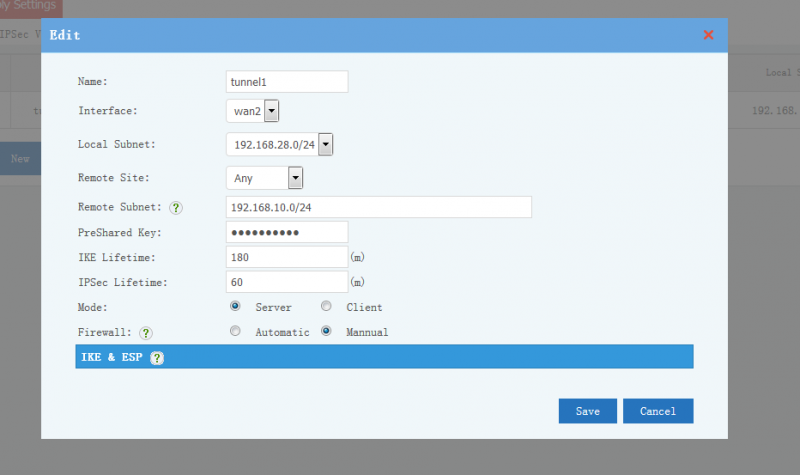
| + | Description of tunnel settings: | ||
| + | * Name: tunnel name. | ||
| + | * Interface: WAN interface to setup the tunnel. | ||
| + | * Local Subnet: local subnet to be connected with the tunnel. | ||
| + | * Remote Site: another side of the tunnel, "Any" to allow any others to connect. The remote site can be an IP address or domain. | ||
| + | * Remote Subnet: remote LAN subnets which will be forwarded to the tunnel. | ||
| + | * PreShared Key: tunnel secret key. With a correct key, the tunnel can not be established. | ||
| + | * Mode: Server -- Waiting for clients to connect, Client -- Initiate connection to a server. | ||
| + | * Firewall: Automatic -- automatic allow clients to access local subnets, Manual -- block VPN clients in default. | ||
| + | * IKE, ESP: algorithm for authentication and transfer. Both sides of the tunnel shall have the same version and algorithm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ipsec01.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Notice''': | ||
| + | * In "manual" mode, tunnel clients are blocked to local subnets. You need to set the firewall rules by yourself in "Config"->"Firewall".(Interface: WAN, type: forward.) | ||
| + | * If you enable DMZ or "Static NAT", please add IPSec port "500,4500" to "port exception". Otherwise, IPSec connections can not be established. | ||
| + | * If the WAN interface has multiple static ip addresses, IPSec only listens in the first IP address. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Tunnel Status == | ||
| + | |||
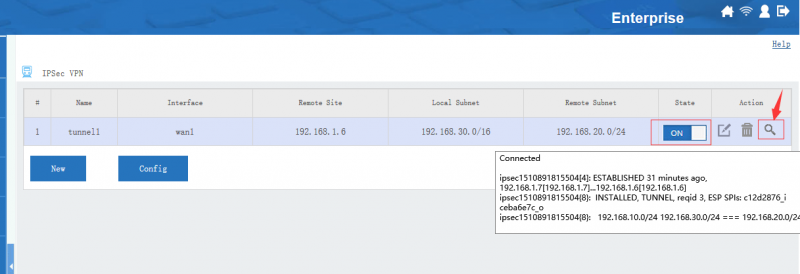
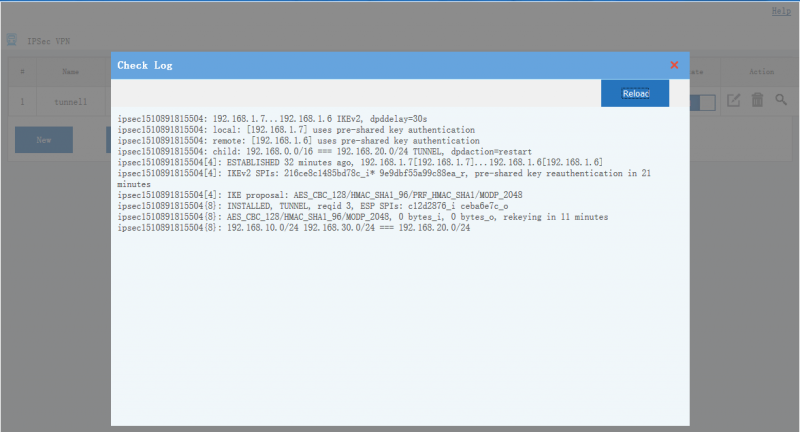
| + | Move your mouse into the "state" icon, you will see the tunnel status and connected clients. You also can click the "view log" icon to check more log details. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ipseclog_01.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ipseclog_02.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == A site to site ipsec vpn sample == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Suppose you have 3 networks: | ||
| + | * Headquarter A, static public ip address, LAN subnet is 192.168.10.0/24. | ||
| + | * Branch B, PPPoE internet access, LAN subnet is 192.168.30.0/24. | ||
| + | * Branch C, PPPoE internet access, LAN subnet is 172.16.1.0/24. | ||
| + | Now let me guide you to build a virtual private network(VPN) for these three locations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Settings for Headquarter A === | ||
| + | * Setup the IPSec tunnel | ||
| + | [[File:ipsec_center01.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ipsec_center02.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Enable forwarding of branches | ||
| + | Without this setting, branches can access headquarter, but no access between branches. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ipsec_center03.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
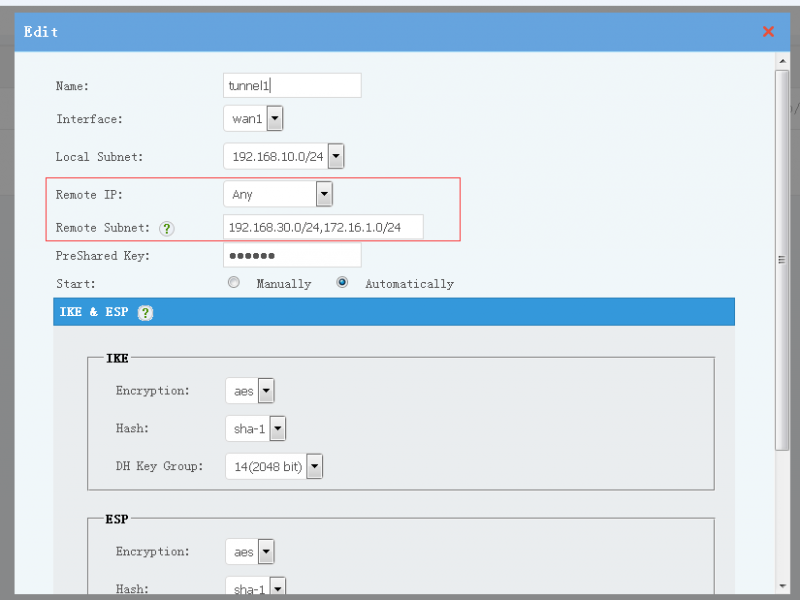
| + | === Branch B === | ||
| + | * Setup the IPSec tunnel | ||
| + | [[File:ipsec_client01.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Branch C === | ||
| + | * Setup the IPSec tunnel | ||
| + | [[File:ipsec_client03.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
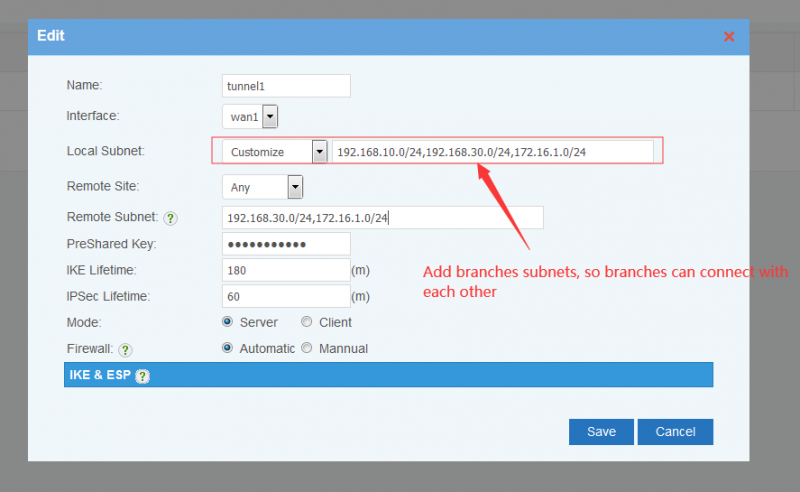
| + | By above steps, AB and AC are now connected. If you also want B and C to communicate with each other, you need to add B&C subnets in headquartor's local subnet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ipsec_client04.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == One-armed Deployment of IPSecVPN == | ||
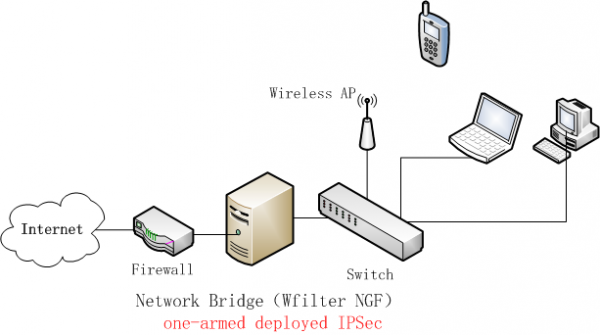
| + | As below network diagram, WFilter NGF is deployed as a network bridge. For IPSec VPN, this is called "one-armed deployment". | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:passby_ipsec.png|600px]] | ||
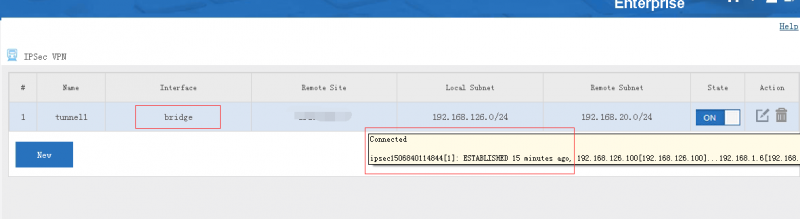
| + | === Setup the IPSec tunnel === | ||
| + | |||
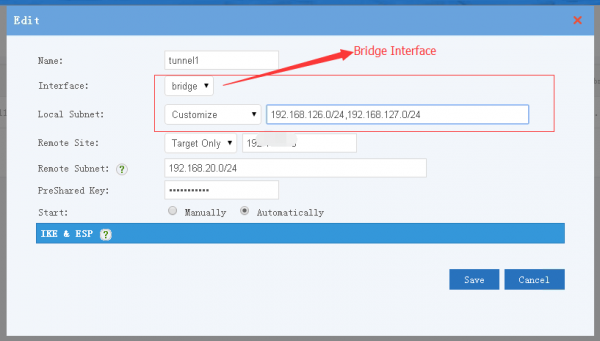
| + | Choose "bridge" as the interface, you might need to setup customize local subnets. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:passby_ipsec02.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Setup port forwarding in gateway === | ||
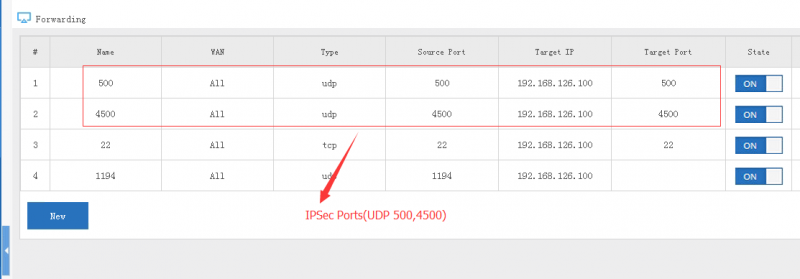
| + | Gateway device needs to map the IPSec ports(UDP 500 and UDP 4500) to WFilter NGF. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:passby_ipsec03.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
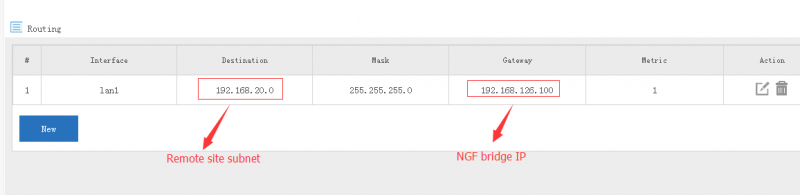
| + | === Setup routing in gateway === | ||
| + | |||
| + | You also need to setup static routing in gateway to point nexthop of remote subnet to WFilter NGF. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:passby_ipsec04.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | IPSec tunnels are available now. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:passby_ipsec05.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:VPN]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:41, 28 November 2019
Contents |
[edit] 1 IPSec Tunnels
This modules can build IPSec tunnels between multiple WFilter NGF networks, and make a secure site-to-site VPN. The number of IPSec Tunnels depends on your hardware performance, there is no software limit on the tunnels number.
[edit] 2 IPSec Tunnel Settings
Before you setup a IPSec tunnel, you need to design your tunnels. For example:
- Suppose you have 3 network: A, B, C.
- A has a static public IP, B and C ip addresses are dynamic.
The solution will be:
- A, B, C shall have differenct subnets. For example: 192.168.10.x, 192.168.20.x, 172.16.1.x.
- Create a tunnel in A network, set "Remote IP" to "Any".
- Create tunnels in B and C networks, set "Remote IP" to A's public ip address.
- Now the tunnels are ready. A, B, C now are in a VPN network. The tunnels are between AB and AC.
- To enable access between B and C, you need to enable FORWARD in A.
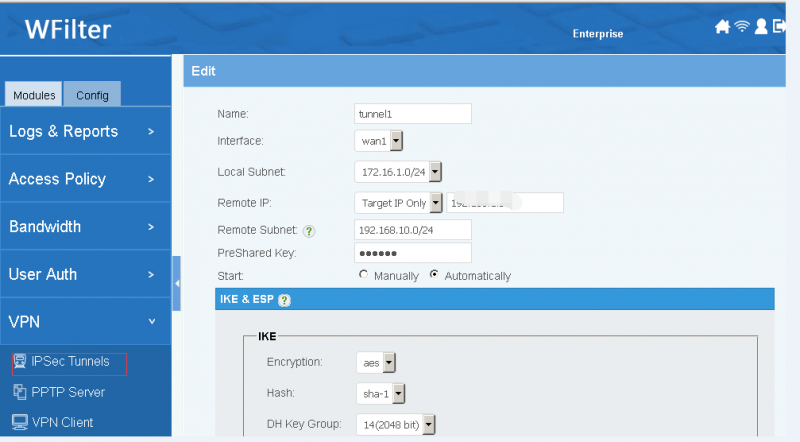
Description of tunnel settings:
- Name: tunnel name.
- Interface: WAN interface to setup the tunnel.
- Local Subnet: local subnet to be connected with the tunnel.
- Remote Site: another side of the tunnel, "Any" to allow any others to connect. The remote site can be an IP address or domain.
- Remote Subnet: remote LAN subnets which will be forwarded to the tunnel.
- PreShared Key: tunnel secret key. With a correct key, the tunnel can not be established.
- Mode: Server -- Waiting for clients to connect, Client -- Initiate connection to a server.
- Firewall: Automatic -- automatic allow clients to access local subnets, Manual -- block VPN clients in default.
- IKE, ESP: algorithm for authentication and transfer. Both sides of the tunnel shall have the same version and algorithm.
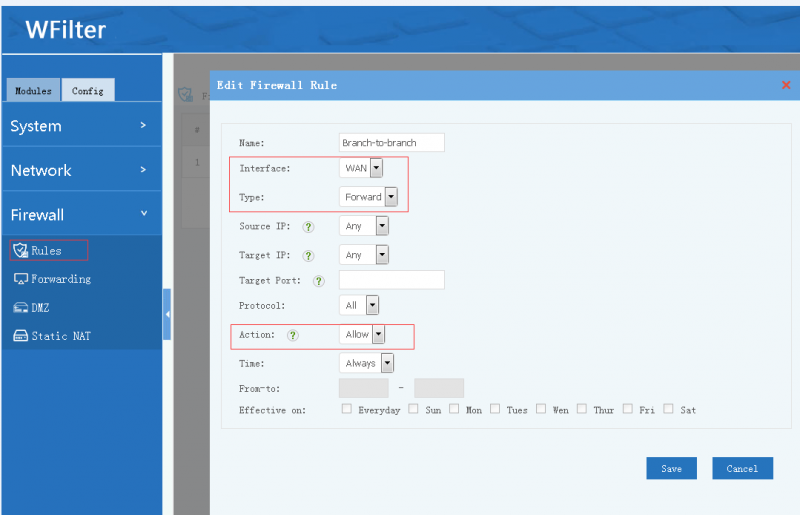
Notice:
- In "manual" mode, tunnel clients are blocked to local subnets. You need to set the firewall rules by yourself in "Config"->"Firewall".(Interface: WAN, type: forward.)
- If you enable DMZ or "Static NAT", please add IPSec port "500,4500" to "port exception". Otherwise, IPSec connections can not be established.
- If the WAN interface has multiple static ip addresses, IPSec only listens in the first IP address.
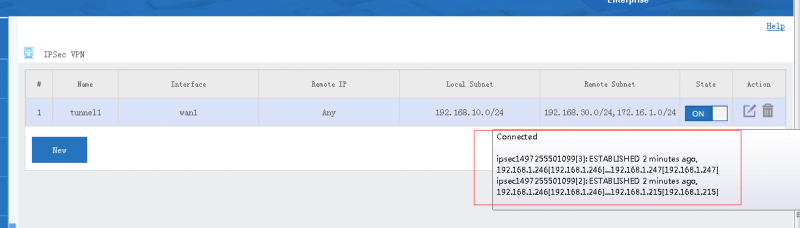
[edit] 3 Tunnel Status
Move your mouse into the "state" icon, you will see the tunnel status and connected clients. You also can click the "view log" icon to check more log details.
[edit] 4 A site to site ipsec vpn sample
Suppose you have 3 networks:
- Headquarter A, static public ip address, LAN subnet is 192.168.10.0/24.
- Branch B, PPPoE internet access, LAN subnet is 192.168.30.0/24.
- Branch C, PPPoE internet access, LAN subnet is 172.16.1.0/24.
Now let me guide you to build a virtual private network(VPN) for these three locations.
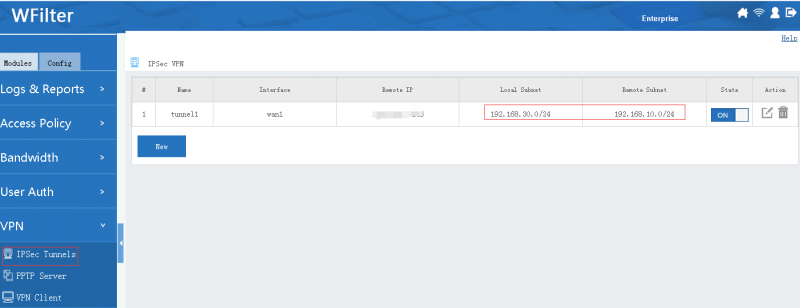
[edit] 4.1 Settings for Headquarter A
- Setup the IPSec tunnel
- Enable forwarding of branches
Without this setting, branches can access headquarter, but no access between branches.
[edit] 4.2 Branch B
- Setup the IPSec tunnel
[edit] 4.3 Branch C
- Setup the IPSec tunnel
By above steps, AB and AC are now connected. If you also want B and C to communicate with each other, you need to add B&C subnets in headquartor's local subnet.
[edit] 5 One-armed Deployment of IPSecVPN
As below network diagram, WFilter NGF is deployed as a network bridge. For IPSec VPN, this is called "one-armed deployment".
[edit] 5.1 Setup the IPSec tunnel
Choose "bridge" as the interface, you might need to setup customize local subnets.
[edit] 5.2 Setup port forwarding in gateway
Gateway device needs to map the IPSec ports(UDP 500 and UDP 4500) to WFilter NGF.
[edit] 5.3 Setup routing in gateway
You also need to setup static routing in gateway to point nexthop of remote subnet to WFilter NGF.
IPSec tunnels are available now.