DMZ Static NAT
From Wiki of WFilter NG Firewall
(Difference between revisions)
(→Port Forwarding) |
(→Port Forwarding) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
** Target Port: "redirected to" port, leave it blank for same as the source port. | ** Target Port: "redirected to" port, leave it blank for same as the source port. | ||
** NAT Reflection: enable or disable NAT reflection. | ** NAT Reflection: enable or disable NAT reflection. | ||
| + | ** Forward to VPN: When enabled, you can forward traffic to clients behind a VPN tunnel. Source IP will be translated to LAN ip address, which can be routed back via a VPN tunnel. | ||
= DMZ = | = DMZ = | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 9 July 2019
Contents |
1 Introduction
"Port Forwarding", "DMZ" and "Static NAT" are all redirecting firewall rules.
- "Port Forwarding" : forword packets on certain port(s).
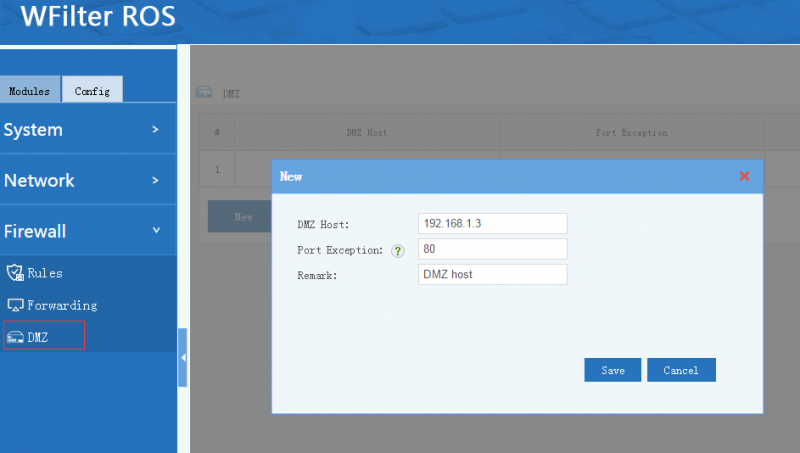
- "DMZ" equals "port forwarding on all ports". Visits to WAN interfaces will be redirected to the DMZ host(except of the excepted ports).
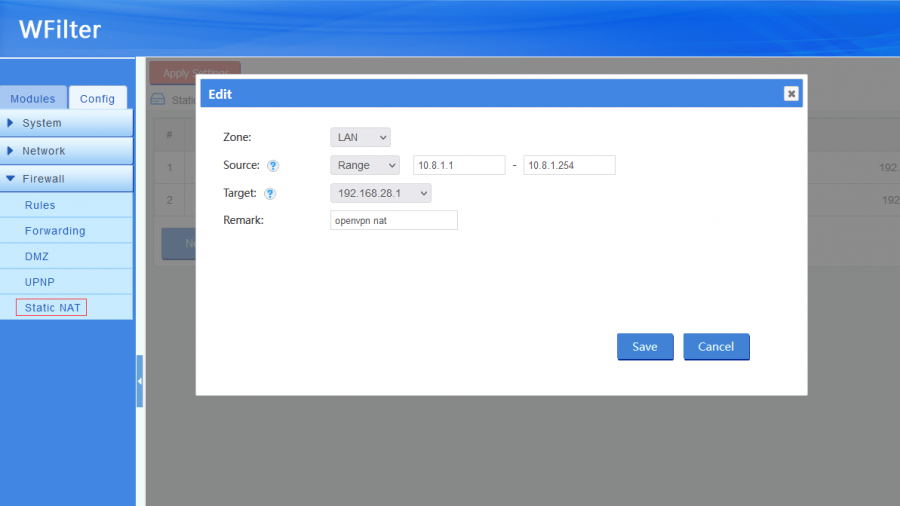
- "Static NAT" provides one-to-one NAT for local hosts.
2 Port Forwarding
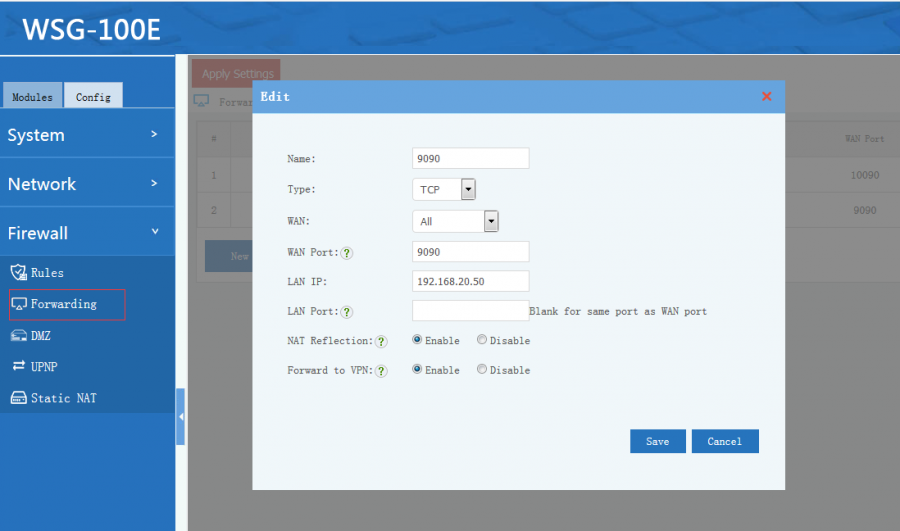
- Forwarding: map a WAN port, port range or all traffic to a local host.
- Type: if type is "all", "source port" and "target port" shall be blank.
- WAN: target WAN IP address.
- Source Port: target port to the WAN interface.
- Target IP: "redirected to" local host IP.
- Target Port: "redirected to" port, leave it blank for same as the source port.
- NAT Reflection: enable or disable NAT reflection.
- Forward to VPN: When enabled, you can forward traffic to clients behind a VPN tunnel. Source IP will be translated to LAN ip address, which can be routed back via a VPN tunnel.
3 DMZ
- DMZ: port forwarding on all ports.
4 Static NAT
You need to define "Local IP" and choose a public IP.
- Single: a single IP(192.168.10.100) or subnet(192.168.10.0/24).
- Range: an IP range.